Consumer electronics function on many individual technologies, many of which tend to become obsolete over time and are replaced by something newer and more capable. However, one bit of technology that has stood the test of time and come out stronger than ever is Bluetooth. This incredibly versatile technology has improved over the years, kept up with the changes, become affordable and compact enough to implement in even the smallest and most affordable devices, and continues to be implemented in just about every gadget we use on a daily basis.
Bluetooth has come a long way since its introduction in the late 1990s, and has gone through various versions and profiles depending on its many use cases. At its core, Bluetooth is a wireless communication technology which allows devices to connect and exchange data over short distances. To better understand the versatility and wide usage capabilities of Bluetooth and its technologies, read on.
Bluetooth versions
Bluetooth started out with its earliest versions (v1.0 and v2.0) which established the technology as a way to wireless send data between devices over short distances at up to 1Mbps – considered fast and revolutionary for its time. Later versions improved upon the speed, stability, pairing reliability, and overall efficiency of the protocol.
Bluetooth 3.0 introduced a particularly useful feature which is popular even today – Low Energy. This protocol allowed certain Bluetooth enabled devices to control the use of energy, thus making Bluetooth much more power-efficient and practical for use in smaller devices. Newer versions such as Bluetooth 5.0 and beyond have further optimised these processes, allowing for fast, stable, efficient, and reliable data transfers between devices.
Bluetooth profiles
Various Bluetooth profiles exist, which specialise the protocol for specific use cases. This includes Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP) which is used to wirelessly transmit audio to speakers, headphones, and car audio systems. This is the most popular and widespread of the profiles, enabling wireless audio in many of the gadgets we use.
ALSO READ: LTE vs Bluetooth smartwatches: Which one should you buy?
Other popular profiles include Audio/Video Remote Control Profile (AVRCP) which works with remotes to control A/V equipment such as TVs and Hi-Fi systems, Basic Printing Profile (BPP) which works to send data to printers, Hands-Free Profile (HFP) for mobile phones to connect to car audio systems, Proximity Profile (PXP) which allows detection of two devices which are close to each other, and more.
What does Bluetooth do?
As mentioned, Bluetooth enables wireless data transfers between devices over short distances. This allows two or more devices to pair, connect, and communicate with each other in real time, which enables wireless functionality for many of the gadgets we use on a daily basis.
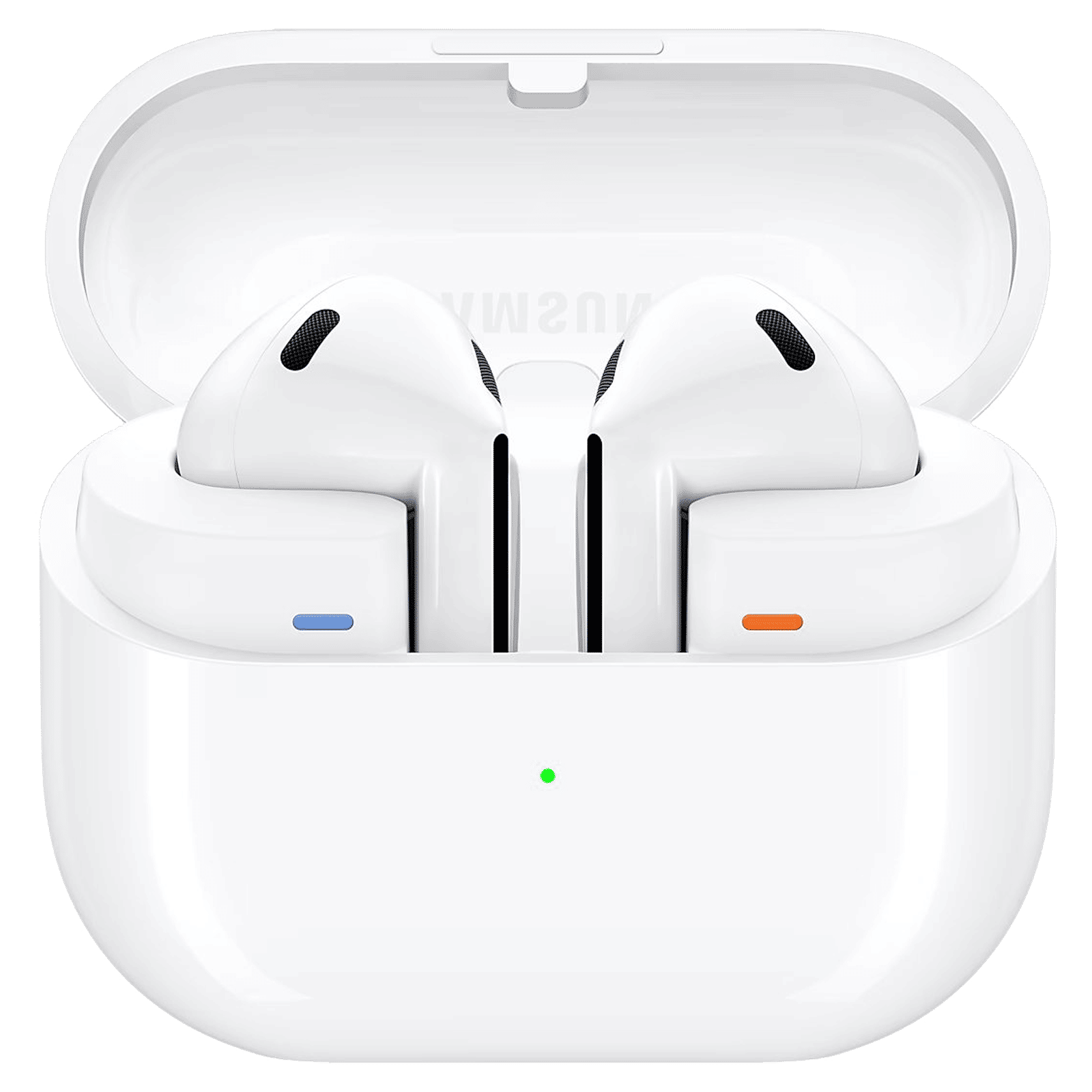
Wireless headphones and earphones commonly use Bluetooth to connect to and receive audio transmissions such as music and voice from our smartphones, tablets, and laptops. You can also use Bluetooth to quickly and conveniently transfer files between two devices, such as images, documents, or audio clips. Even our television remotes are often Bluetooth-enabled, and don’t need to be pointed at the TV to work; we can use the remote anywhere within a short range of the TV, and we can also use it to transmit audio such as voice commands.
Bluetooth has applications even in smart home and home automation, wearable gadgets such as smartwatches and smart rings, and automotive devices such as smart keys and infotainment systems. It’s an extremely capable and versatile technology that powers so many of the devices we use every day.
Unleash your inner geek with Croma Unboxed
Subscribe now to stay ahead with the latest articles and updates
You are almost there
Enter your details to subscribe

Happiness unboxed!
Thank you for subscribing to our blog.
Disclaimer: This post as well as the layout and design on this website are protected under Indian intellectual property laws, including the Copyright Act, 1957 and the Trade Marks Act, 1999 and is the property of Infiniti Retail Limited (Croma). Using, copying (in full or in part), adapting or altering this post or any other material from Croma’s website is expressly prohibited without prior written permission from Croma. For permission to use the content on the Croma’s website, please connect on contactunboxed@croma.com
- Related articles
- Popular articles














Ali Pardiwala
Comments